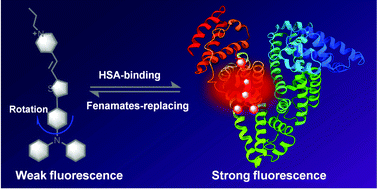
Human serum albumin (HSA) can bind with numerous drugs, leading to a significant influence on drug pharmacokinetics as well as undesirable drug–drug interactions due to competitive binding. Probing the HSA drug binding site thus offers great opportunities to reveal drug–HSA binding profiles. In the present study, a fluorescent probe (E)-4-(2-(5-(4-(diphenylamino)phenyl)thiophen-2-yl)vinyl)-1-propylpyridin-1-ium (TTPy) has been prepared, which exhibits enhancement of deep-red to near-infrared (NIR) fluorescence upon HSA binding. The competitive binding assay indicated that TTPy can target the HSA binding site of fenamates, a group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), with moderate binding affinity (1.95 × 106 M−1 at 303 K). More interestingly, TTPy enables fluorescent labeling of HSA upon visible light irradiation. This study provides promising ways for HSA drug binding site identification and photochemical protein labeling.