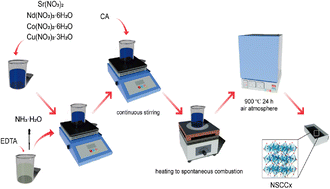
Nd0.6Sr0.4Co1−xCuxO3−δ (x = 0, 0.05, 0.1, 0.15, 0.2) (NSCCx) was prepared by replacing Co with Cu. Its chemical compatibility, electrical conductivity, and electrochemical properties were studied by X-ray powder diffractometry, scanning electron microscopy, and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. The conductivity, AC impedance spectra, and output power of the single cell were tested in an electrochemical workstation. Results showed that the thermal expansion coefficient (TEC) and electrical conductivity of the sample decreased with the increase in Cu content. The TEC of NSCC0.1 decreased by 16.28% in the temperature range of 35 °C–800 °C, and its conductivity was 541 S cm−1 at 800 °C. Furthermore, a single cell was constructed with NSCCx as the cathode, NiO-GDC as the anode, and GDC as the electrolyte. The peak power of the cell at 800 °C was 444.87 mW·cm−2, which was similar to that of the undoped sample. Compared with the undoped NSCC, NSCC0.1 showed lower TEC while maintaining its output power. Therefore, this material can be used as a cathode for solid oxide fuel cells.