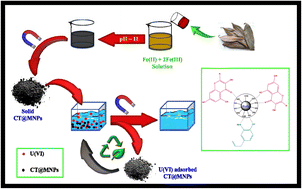
U(VI) removal using cost-effective (production cost: $14.03 per kg), biocompatible, and superparamagnetic Cinnamomum tamala (CT) leaf extract-coated magnetite nanoparticles (CT@MNPs or CT@Fe3O4 nanoparticles) from water resources was studied. From pH-dependent experiments, the maximum adsorption efficiency was found to be at pH 8. Isotherm and kinetic studies were performed and found to follow Langmuir isotherm and pseudo-second order kinetics, respectively. The maximum adsorption capacity of CT@MNPs was calculated to be 45.5 mg of U(VI) per g of nanoparticles (NPs). Recyclability studies suggest that over 94% sorption was retained even after four consecutive cycles. The sorption mechanism was explained by the point of the zero-charge experiment and the XPS measurement. Additionally, calculations using density functional theory (DFT) were carried out to support the experimental findings.