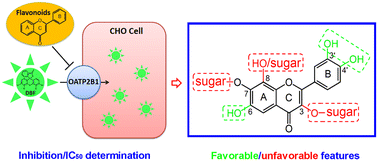
Human organic anion transporting polypeptide 2B1 (OATP2B1) is a crucial transporter for the absorption and disposition of many drugs. Its inhibition by small molecules may alter the pharmacokinetic profile of its substrate drugs. In this study, the interactions of 29 common flavonoids with OATP2B1 were explored using the fluorescent substrate 4′,5′-dibromofluorescein and structure–activity relationship analysis. Our results showed that flavonoid aglycones interact with OATP2B1 more strongly than their 3-O- and 7-O-glycoside counterparts, as hydrophilic and bulky groups at these two sites are detrimental to flavonoids' binding with OATP2B1. In contrast, hydrogen-bond forming groups at the C-6 position of ring A and the C-3′ and C-4′ positions of ring B could strengthen the interaction of flavonoids with OATP2B1. However, a hydroxyl or sugar moiety at the C-8 position of ring A is unfavorable. Our results also indicated that flavones usually interact more strongly with OATP2B1 than their 3-hydroxyflavones (flavonols). The obtained information could be useful for the prediction of additional flavonoids for their interaction with OATP2B1.