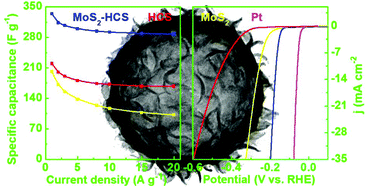
Herein, we report the synthesis of hybrid nanostructures obtained by densely growing MoS2 nanosheet layers on hydrophobic hollow carbon spheres (abbreviated as MoS2-HCS) through a solvothermal method. The morphologies and compositions of the MoS2-HCS hybrid are well investigated. The electrochemical performance of the MoS2-HCS sphere is investigated in both supercapacitors and the hydrogen evolution reaction. The MoS2-HCS exhibits a larger specific capacitance of 334 F g−1 than the bare MoS2 of 204 F g−1 at 1 A g−1, an improved rate capability of 86% from 1 to 20 A g−1 and a stable cycling performance of 87% capacitance retention after 5000 cycles when assembled in a supercapacitor. In addition, MoS2-HCS also show enhanced electrocatalytic activity for the electrochemical hydrogen evolution reaction in acidic media.