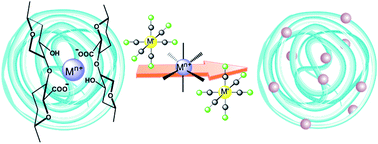
A new approach for the synthesis of Prussian blue type nanoparticles containing nanocomposites in the form of beads or films, as well as their corresponding aqueous colloids, was developed by using a water-soluble alginate matrix as a template and as a stabilizing agent. This method consists of the step-by-step building of a cyanometallate network in the pores of Mn+/alginate ionotropic gels in order to obtain a large range of nanocomposites containing cyano-bridged coordination polymer nanoparticles Mn+/[M′(CN)m]3−/alginate (where Mn+ = Ni2+, Cu2+, Mn2+, Fe2+, Eu3+ and M′ = Fe3+, Cr3+ (m = 6), Mo5+ (m = 8)). The nanocomposite beads and films, as well as the corresponding aqueous colloidal solutions, were studied by infrared (IR), UV/visible spectroscopy, and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) analyses, which reveal the presence of homogeneously dispersed uniformly sized cyano-bridged coordination polymer nanoparticles of 3–7 nm. These nanocomposite beads and films present superparamagnetic, spin-glass or paramagnetic behaviour depending on the nature of the metal ions used. In addition, the Eu3+-containing nanocomposites are room temperature optically active emitters displaying a characteristic 5D0 → 7F0–4 transition.