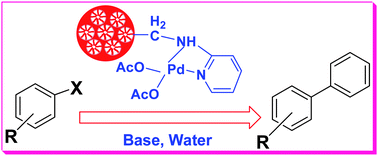
We report the synthesis and catalytic activities of a mesoporous silica nanosphere supported palladiumII 2-aminopyridine complex (Pd-AMP-MSN). First, chloroalkyl functionalized mesoporous silica nanospheres (Cl-MSN) is prepared by an in situ co-condensation reaction of tetraethyl orthosilicate (TEOS) with ((chloromethyl)phenylethyl)trimethoxysilane (CMPE-TMS) using cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) as the structure directing agent. The reaction of Cl-MSN with 2-aminopyridine followed by complexation with palladium acetate produces the catalyst Pd-AMP-MSN. FTIR spectroscopic analysis confirms the presence of 2-aminopyridine functionality inside the mesopores of the Pd-AMP-MSN. Nitrogen adsorption–desorption and X-ray diffraction analyses reveal mesoporous structures of the Pd-AMP-MSN catalyst with a specific surface area of 372 m2 g−1, a pore volume of 0.172 cm3 g−1 and a narrow pore size distribution (D ∼ 1.92 nm). FESEM and HRTEM results indeed show the formation of nanospheres with mesoporous structures. This catalytic system exhibits excellent activity in Suzuki–Miyaura cross-coupling reactions of aryl iodides, aryl bromides and also aryl chlorides with phenylboronic acids in water medium with high yields. This Pd-AMP-MSN catalyst could be quantitatively recovered by simple filtration and is found to be highly active without any significant loss of its catalytic activity in eight consecutive runs.