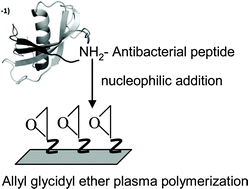
In this study, robust antibacterial coatings were created on stainless steel through the covalent grafting of antibacterial peptides onto an organic–polymeric interlayer deposited by RF-glow discharge plasma. X-Ray photoelectron spectroscopy was used to characterize and optimize the two steps of the coating process. The biocidal activity of these surfaces was demonstrated against both Gram+ and Gram− bacteria using ISO tests. 3 to 6 log10 reductions of both Gram+ and Gram− bacterial strains were obtained compared to uncoated stainless steel and depending on the particular antibacterial peptide immobilized. Importantly the antibacterial surfaces were resistant to several cleaning conditions. The latter is significant as the stability of such antibacterial surfaces in close to real life conditions is a major concern and leaching, de-lamination, rearrangement and ageing of the coating can lead to insufficient long term biofilm resistance of the surface.