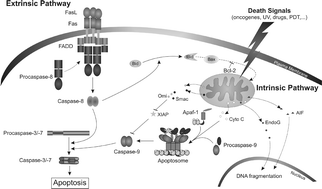
Photodynamic therapy is an approved treatment for several types of tumors and certain benign diseases, based on the use of a light-absorbing compound (photosensitizer) and light irradiation. In the presence of molecular oxygen, light-activation of the photosensitizer, which accumulates in cancer tissues, leads to the local production of reactive oxygen species that kill the tumor cells. Mitochondria are central coordinators of the mechanisms by which PDT induces apoptosis in the target cells. Recent studies indicate that concomitant to the permeabilization of the outer mitochondrial membrane (which leads to the release of several apoptogenic factors in the cytosol and to the activation of effector caspases), regulatory signaling pathways are activated in a photosensitizer, PDT dose and cell-dependent fashion. Signaling pathways regulated by members of mitogen activated protein kinases and their downstream targets, such as cyclooxygenase-2, appear to critically modulate cancer cell sensitivity to PDT. Understanding the molecular events that contribute to PDT-induced apoptosis, and how cancer cells can evade apoptotic death, should enable a more rationale approach to drug design and therapy.