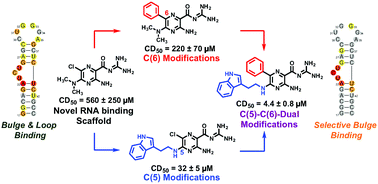
Diversification of RNA-targeted scaffolds offers great promise in the search for selective ligands of therapeutically relevant RNA such as HIV-1 TAR. We herein report the establishment of amiloride as a novel RNA-binding scaffold along with synthetic routes for combinatorial C(5)- and C(6)-diversification. Iterative modifications at the C(5)- and C(6)-positions yielded derivative 24, which demonstrated a 100-fold increase in activity over the parent dimethylamiloride in peptide displacement assays. NMR chemical shift mapping was performed using the 2D SOFAST-[1H-13C] HMQC NMR method, which allowed for facile and rapid evaluation of binding modes for all library members. Cheminformatic analysis revealed distinct differences between selective and non-selective ligands. In this study, we evolved dimethylamiloride from a weak TAR ligand to one of the tightest binding selective TAR ligands reported to date through a novel combination of synthetic methods and analytical techniques. We expect these methods to allow for rapid library expansion and tuning of the amiloride scaffold for a range of RNA targets and for SOFAST NMR to allow unprecedented evaluation of small molecule:RNA interactions.