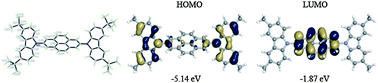
Tetrahydropyrene and pyrene have been functionalized in their 2,7-positions with carbazole and 3,6-di-tert-butylcarbazole groups, and the properties of these new compounds are compared to analogous carbazole and 3,6-di-tert-butylcarbazole derivatives of benzene and biphenyl using X-ray crystallography, UV-vis absorption and fluorescence spectroscopy, electrochemistry, and quantum-chemical calculations. The absorption spectra are similar to those of their biphenyl-bridged analogues, although TD-DFT calculations indicate a different description of the excited states in the pyrene case, with the lowest observed absorption no longer corresponding to the S0 → S1 transition. The 3,6-di-tert-butylcarbazole compounds show reversible electrochemical oxidations; the benzene, biphenyl, tetrahydropyrene, or pyrene bridging groups have little impact on the first oxidation potential. Bilayer organic light-emitting diodes incorporating the tetrahydropyrene and pyrene derivatives as emitters show deep-blue electroluminescence.