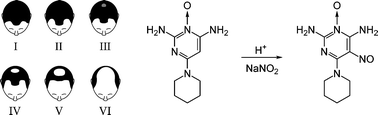
Minoxidil (2,4-diamino-6-(piperidin-1′-yl)pyrimidine N(3)-oxide; CASRN 38304-91-5) is a bioactive molecule with several nitrosatable groups widely used as an antihypertensive and antialopecia agent. Here the nitrosation of minoxidil was investigated. The conclusions drawn are as follows: (i) In the pH = 2.3–5.0 range, the minoxidil molecule undergoes aromatic C-nitrosation by nitrite. The dominant reaction was C-5 nitrosation through a mechanism that appears to consist of an electrophilic attack on the nitrosatable substrate by H2NO2+/NO+, followed by a slow proton transfer; (ii) the reactivity of minoxidil as a C-nitrosatable substrate proved to be 7-fold greater than that of phenol, this being attributed to the preferred para- and ortho-orientations of the two -NH2groups at positions 2 and 4 of the minoxidil molecule, which activate electrophilic substitution in the C-5 position through their mesomeric effect. The N-nitrosominoxidil resulting from the nitrosation could be potentially harmful to the minoxidil users.