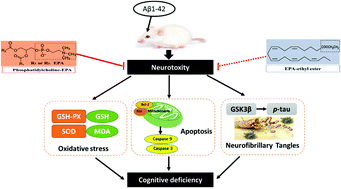
Abundant studies have highlighted the protective effects of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), in the form of glycerolipids (glycerophosphatides and triglycerides) and DHA-ethyl esters (DHA-EE) in Alzheimer's disease (AD); however, eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) has rarely been implicated. In the present study, we compared the effects of dietary EPA in the form of phosphatidylcholine (EPA-PC) and EE with DHA-EE (DHA/EPA = 60 mg kg−1 d−1, i.g., 20 days) on cognitive deficits in AD rats. EPA-PC, rather than EPA-EE, significantly improved Aβ-induced cognitive impairment and has a comparable effect with DHA-EE. Further research indicated that EPA-PC and DHA-EE could significantly decrease lipid peroxidation levels, alleviate mitochondria-dependent apoptosis, and inhibit the hyperphosphorylation of tau mediated by GSK3β. These findings suggest that EPA in the form of phosphatidylcholine rather than an ethyl ester has a comparable effect with DHA in improving cognitive impairment in Aβ1–42-induced AD rats.