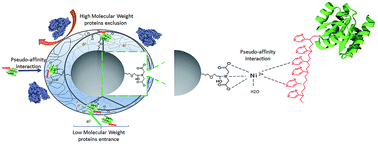
Herein, silica nanoparticles were synthesized and chemically modified with iminodiacetic acid (IDA) and Ni2+ ions surrounded by a bis-acrylamide polymeric shell to obtain a new core–shell immobilized metal affinity chromatography (IMAC) based material. These Ni2+–IDA-core–shell silica nanoparticles (Ni2+–IDA-CSS-NP) represent a new alternative for purification of His-tagged proteins and exclusion of high molecular weight (HMW) proteins at the same time. Nanoparticles presented a final size of 479.6 ± 6.9 nm determined by dynamic light scattering (DLS) and a surface charge of −37.2 ± 0.5 mV. Successful incorporation of the different compounds at every phase of synthesis was evidenced by ATR-FTIR analysis. Ni2+–IDA-CSS-NP were used for isolation of His-tagged spo0F (6His-spo0F) from E. coli lysate. Ni2+–IDA-CSS-NP presented a capacity of 4.16 ± 0.45 μg mg−1. Purification of 6His-spo0F with high selectivity and the effective exclusion of HMW proteins were evidenced by SDS-PAGE and validated through mass spectrometry analysis.