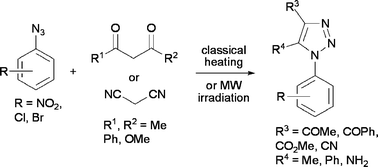
Reactions were performed from aryl azides on the one hand, and activated alkenes coming from β-dicarbonyl compounds or malonodinitrile on the other hand, either with recourse to conventional heating or to microwave activation, to afford 1-aryl-1H-1,2,3-triazoles. The mechanism and the regioselectivity of the reactions involving β-dicarbonyl compounds have been theoretically studied using DFT methods at the B3LYP/6-31G* level: they are domino processes comprising a tautomeric equilibrium of the β-dicarbonyl compounds with their enol forms, a 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition of the enol forms with the aryl azides (high activation energy), and a dehydration process (lower activation energy). The effect of non-conventional activation methods on the degradation of 1,2,3-triazolines was next studied experimentally. Finally, some of the 1,2,3-triazoles such synthesized were evaluated for their bactericidal and cytotoxic activities.