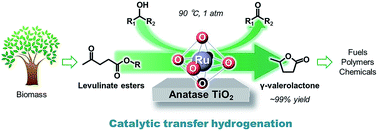
Production of γ-valerolactone (GVL) from levulinate esters and several alcohols as hydrogen donors via a catalytic transfer hydrogenation (CTH) process was performed over supported ruthenium hydroxide catalysts. Among the catalysts examined, Ru(OH)x supported on high-surface-area, anatase TiO2 containing highly-dispersed ultrasmall Ru(OH)x nano-clusters was found to be the most active catalyst, which converted levulinate esters to GVL in an almost quantitative yield under mild reaction conditions with low catalyst loading. Addition of heterogeneous bases could afford a faster reaction rate in GVL production by accelerating the following intramolecular dealcoholation step. The catalyst was reusable over repeated catalytic cycles without loss of catalytic performance, making this material a potential candidate for efficient GVL production under ambient reaction conditions.