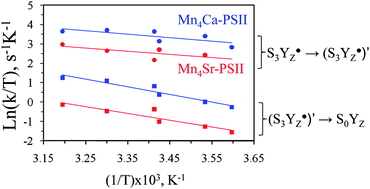
The role of Ca2+ in the Photosystem IIwater oxidation mechanism has been investigated in the higher redox states of the enzyme. The involvement of Ca2+ in structuring the environment of the tyrosine YZ in the S3 state has been investigated by studying the effect of a Ca/Sr exchange by pulse-EPR spectroscopy. It is shown that Ca and Yz are involved in a common hydrogen bond network in S3. The comparison of the temperature dependence of the rate of the water oxidation reaction shows that the slowdown of the S3YZ˙ → S0 transition in Sr-PSII mainly arises from a decrease of the entropic part of the ΔG# of the reaction. This suggests that Ca/Sr exchange perturbs the distribution of the conformational microstates and thereby hinders the overall water splitting process.