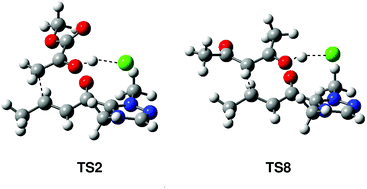
The NHC catalysed nucleophilic additions of enols to α,β-unsaturated acyl-azolium intermediates have been investigated using DFT methods at the MPWB1K/6-31G** computational level. In the direct and the conjugate additions, formation of a hydrogen bond (HB) with the carboxyl oxygen is not sufficient to favour the C–C bond formation as a consequence of the low nucleophilic character of enols. Interestingly, when enols form a HB with the chloride counterion, the activation energies associated with the conjugate addition decrease as a consequence of the increased nucleophilic character of enols and the increased electrophilic character of the ‘acyl-azolium + Cl’ ion pair. Analysis of the DFT reactivity indices allows establishing a base catalysed C–C bond-formation step promoted by the chloride counterion.