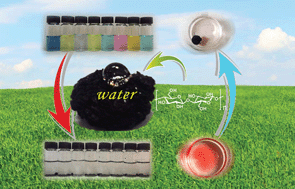
Carbon aerogels have attracted considerable attention in fundamental investigation and potential applications in a myriad of fields. We present a novel approach for the synthesis of cellulose-based carbon aerogels by dissolution, gelation, regeneration, freeze-drying and carbonization of cellulose. The carbon aerogels obtained here possess the characteristics of high surface area (500 m2 g−1), hydrophobicity, and fire-resistance. In addition, the carbon aerogels show excellent adsorption capacity and selectivity for removal of oils, organic solvents, a variety of dyes, and heavy ions, so they could be used as promising adsorbents for sewage treatment. Especially for malachite green and Cu(II), the adsorption capacities can reach up to 1947 mg g−1 and 801 mg g−1, respectively, which far surpass other aerogels previous reported.