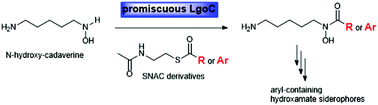
More than 500 siderophores are known to date, but only three were identified to be aryl-containing hydroxamate siderophores, legonoxamines A and B from Streptomyces sp. MA37, and aryl ferrioxamine 2 from Micrococcus luteus KLE1011. Siderophores are produced by microorganisms to scavenge iron from the environment, thereby making this essential metal nutrient available to the microbe. We demonstrate here that LgoC from MA37 is responsible for the key aryl-hydroxamate forming step in legonoxamine biosynthesis. Biochemical characterization established that LgoC displays considerable promiscuity for the acylation between N-hydroxy-cadaverine and SNAC (N-acetylcysteamines) thioester derivatives.