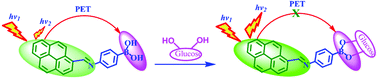
An efficient D-glucose selective pyreneimine monoboronic acid probe, based on a photoinduced electron transfer (PET) mechanism, has been developed. The analyses of the spectral changes in the UV-Vis. and fluorescence studies suggest that probe 1 shows an excellent response to D-glucose with a high association constant in a DMSO medium. Photoinduced electron transfer (PET) from the pyreneimine donor to the boronic acid acceptor present is proposed to be responsible for the observed sensing response, which is rationalized by time dependent density functional theory (TD-DFT) calculations. The present sensing system is also successfully applied to the detection of D-glucose in glucose injections.