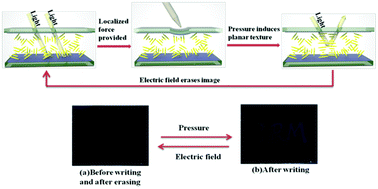
We present a pressure-sensitive polymer dispersed cholesteric liquid crystal (PDCLC) device, in which a cholesteric liquid crystal (ChLC) is encapsulated by a polymer network via an ultraviolet photopolymerization induced phase separation method. The effects of the acrylate monomer concentration and functionality on the network morphology, and the electro-optic behaviour of the PDCLC device were studied. The results demonstrated that the electro-optic properties, including reflectivity and the contrast ratio of the pressure-sensitive device, were improved as the ChLC droplet size increased. An appropriate network density in the system limited the flow of the ChLC and allowed high-resolution lines to be drawn on the device. Additionally, the critical pressure switching of the device from a focal conic state to a planar state was investigated. The device developed in this study has promising applications in many fields such as flexible display devices and optical sensors.