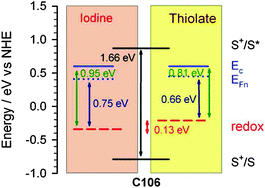
To overcome the intrinsic shortcomings of the traditional iodide–triiodide redox couple and pursue a further performance improvement, intense efforts have been made to exploit alternative redox shuttles in dye-sensitized solar cells (DSCs). Herein, we report an energetic and kinetic view of DSCs when the iodine electrolyte is substituted with its thiolate counterpart and identify that a conventional platinum counter electrode presents low catalytic activity for the thiolate electrolyte, featuring a high charge transfer resistance found at the platinized fluorine-doped tin oxide (FTO). We employ conductive carbon black with several polymers to fabricate highly active composite catalysts for thiolate regeneration. The use of a highly active conductive carbon black and polymerized 3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene composition as a counter electrode combined with a high-absorptivity ruthenium dye C106 sensitized titania film has generated a DSC with an organic thiolated electrolyte, exhibiting an overall power conversion efficiency of 7.6% under AM1.5G full sunlight.