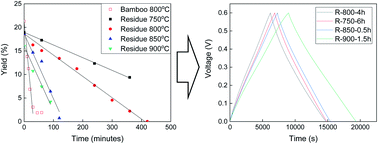
CO2 activation of the solid residue of bamboo after hydrothermal treatment, which is used for the production of xylo-oligosaccharide, was investigated in detail. The reference temperature for carbonization and CO2 activation was 800 °C. The activated carbon from a solid residue was demonstrated to have a higher potential for making EDLC electrodes than bamboo activated carbon thanks to its very low ash content (almost 0) and high porosity structure with a BET surface area up to ca. 2150 m2 g−1. The electrochemical performance of ELDC electrodes prepared from solid residue-derived activated carbon in 1 M H2SO4 aqueous solution was measured and well compared with carbon from bamboo. Through investigation, it is clear that the capacitance of the electrode made from the solid residue has a better capacity than that of raw bamboo.