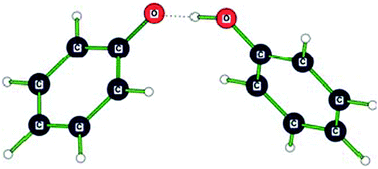
The phenol–phenolate anionic complex was studied in vacuo by negative ion photoelectron spectroscopy using 193 nm photons and by density functional theory (DFT) computations at the ωB97XD/6-311+G(2d,p) level. We characterize the phenol–phenolate anionic complex as a proton-coupled phenolate pair, i.e., as a low-barrier hydrogen bond system. Since the phenol–phenolate anionic complex was studied in the gas phase, its measured hydrogen bond strength is its maximal ionic hydrogen bond strength. The D(PhO−⋯HOPh) interaction energy (26–30 kcal mol−1), i.e., the hydrogen bond strength in the PhO−⋯HOPh complex, is quite substantial. Block-localized wavefunction (BLW) computations reveal that hydrogen bonded phenol rings exhibit increased ring π-electron delocalization energies compared to the free phenol monomer. This additional stabilization may explain the stronger than expected proton donating ability of phenol.