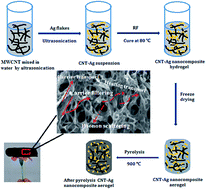
New conducting aerogels based on carbon nanotube (CNT) and silver (Ag) nanocomposites have been systematically investigated. The unique 3D network structures of the aerogels enable a remarkable reduction in their thermal conductivities. It is shown that the CNT–Ag nanocomposite aerogels (CNTANAs) possess low thermal conductivities of only 0.06 to 0.095 W m−1 k−1 with various Ag contents at room temperature; these values are much lower than those of other reported CNT and Ag composites with non-porous structures. Moreover, the electrical conductivities and Seebeck coefficients of the CNTANAs can be simultaneously enhanced by increasing the Ag content in the unique structure; this overcomes a drawback of bulk semiconductors wherein increasing electrical conductivity is generally accompanied by a reduced Seebeck coefficient and enhances the thermal conductivity. As a result, this strategy results in a maximum ZT value of 0.011. This ZT value is about 1 order of magnitude higher than that of the carbon aerogel and 2 orders of magnitude higher than that of the silver/polymer composites and CNT/polymer composites. At the same time, the fragile solid skeleton and highly open-cell foam structure of the CNTANAs lead to low apparent density (∼130 kg m−3). In this study, our study offers a new preparation method for TE materials, which will broaden the development of this facile and novel category of lightweight TE material.