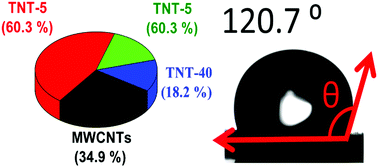
Capacitive deionization (CDI) is being progressed as an auspicious ion removal technique from brackish and seawater. Herein, we introduce a novel one-step facile chemical approach to fabricate tubular architectured composite electrodes made of both Titania and Multiwalled carbon nanotubes (TNTs/MWCNTs). The composites have been exploited, for the first time, as electrode materials for capacitive deionization. The composite electrodes were fully characterized via Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy (FESEM), Raman spectroscopy, X-ray Diffraction (XRD), X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS) techniques, and Nitrogen Sorption. The electrochemical response was investigated by using Cyclic Voltammetry (CV), Galvanostatic Charge and Discharge (GCD), and Potentio-Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (PEIS) measurements. The fabricated composite electrodes containing 5 wt% TiO2 nanotubes showed remarkable specific capacitance, conductivity, reversibility, and durability compared to pristine MWCNTs and other MWCNT-based composite electrodes reported in the literature. The desalination capability of the composite electrode was investigated using batch mode operation. The electrosorption capacity of the composite electrode containing 5 wt% TiO2 nanotubes (13.2 mg g−1) is approximately two fold larger than that of pristine MWCNTs (7.7 mg g−1), indicating an improved desalination efficiency. Therefore, the fabricated TNT/MWCNT composite electrode is a promising candidate for CDI technology.