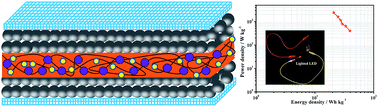
A novel redox-mediated gel polymer (PVA–H2SO4–ARS) is prepared by introducing alizarin red S (ARS) into a polyvinyl alcohol–sulphuric acid (PVA–H2SO4) gel polymer system, and a symmetric supercapacitor using the gel polymer as electrolyte and activated carbon as electrode is also assembled. The PVA–H2SO4–ARS gel polymer has excellent bending, compressing and stretching mechanical properties. The introduction of ARS increases the ionic conductivity of the gel polymer, and improves the pseudocapacitance of the supercapacitor. As expected, the PVA–H2SO4–ARS gel polymer electrolyte has a high conductivity of 33.3 mS cm−1, and the supercapacitor with PVA–H2SO4–ARS electrolyte exhibits a larger electrode specific capacitance (441 F g−1) than the one with PVA–H2SO4 electrolyte (160 F g−1) at the same current density of 0.5 A g−1. Simultaneously, the supercapacitor with PVA–H2SO4–ARS electrolyte exhibits high energy density (39.4 W h kg−1) and good charge–discharge stability. Therefore, this novel electrolyte has good prospects for improving the electrochemical performance of an energy storage device.