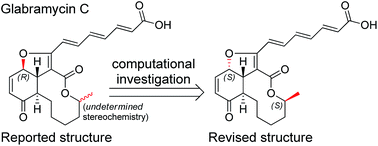
Glabramycins B and C are antibacterial natural products produced by the fungal organism Neosartorya glabra. Their stereochemical structures have not been completely defined to date. In this work, DFT calculations are employed to predict the expected carbon-13 NMR chemical shifts and key vicinal proton–proton coupling constants for all of the candidate stereoisomers. By comparison with experimentally measured values, the complete relative stereochemical configurations for glabramycins B and C are established.