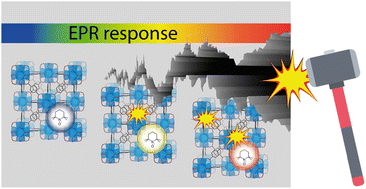
Probes sensitive to mechanical stress are in demand for the analysis of pressure distribution in materials, and the design of pressure sensors based on metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) is highly promising due to their structural tunability. We report a new pressure-sensing material, which is based on the UiO-66 framework with trace amounts of a spin probe (0.03 wt%) encapsulated in cavities. To obtain this material, we developed an approach for encapsulation of stable nitroxide radical TEMPO ((2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidin-1-yl)oxyl) into the micropores of UiO-66 during its solvothermal synthesis. Pressure read-out using electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) spectroscopy allows monitoring the degradation of the defected MOF structure upon pressurization, where full collapse of pores occurs at as low a pressure as 0.13 GPa. The developed methodology can be used in and ex situ and provides sensitive tools for non-destructive mapping of pressure effects in various materials.