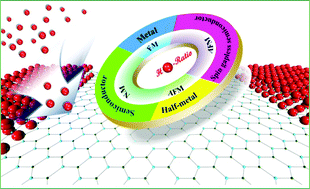
Based on first-principles computations, the geometries, stabilities, electronic and magnetic properties of fully and partially hydrogenated silicon carbide nanoribbons (SiCNRs) were investigated. Independent of the ribbon width, the fully hydrogenated zigzag and armchair SiCNRs are all non-magnetic wide-band-gap semiconductors. By hydrogenating zigzag SiCNRs (zSiCNRs) from the edge(s) step by step, we have constructed partially hydrogenated zSiCNRs that can be viewed as the combination of hydrogenated and pristine zigzag SiC chain building blocks along the periodical direction. The computed results reveal that greatly enriched electronic and magnetic properties can be achieved in zSiCNRs: the transition of the antiferromagnetic spin gapless semiconductor (SGS)–ferromagnetic metal–antiferromagnetic half-metal–non-magnetic semiconductor can be achieved by controlling the hydrogenation pattern and ratio. Notably, this is the first time that the concept of successive hydrogenation starting from the edge(s) is proposed as an effective approach to fine-tune the electronic and magnetic behaviors of SiCNRs. These appealing features, especially the diverse electronic and magnetic transitions, in the unitary SiCNR-based nanostructures may provide tremendous potential applications for integrated multi-functional and spintronic nanodevices.